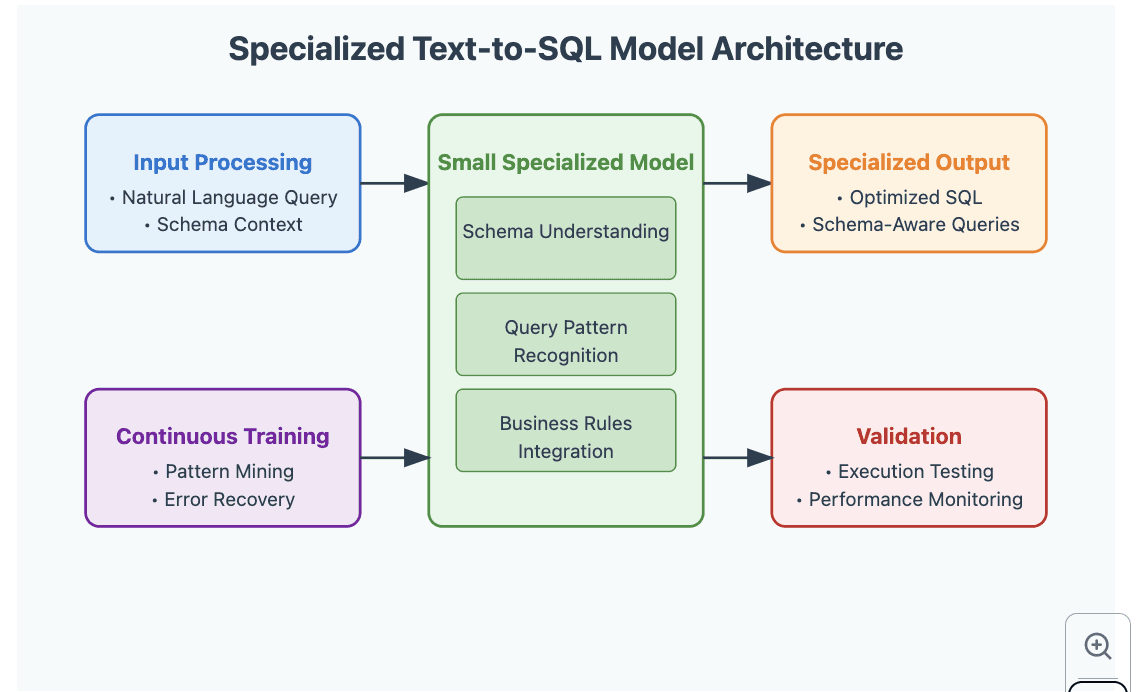
Why Small Models Can Outperform Large Ones
When dealing with a specific database schema, smaller models (< 3B parameters) can actually outperform larger models for several reasons:
Focused Knowledge
Less parameter space wasted on irrelevant domains
Stronger pattern recognition for specific schema patterns
Better memorization of common query templates
Schema-Specific Advantages
Can memorize entire schema structure
Learn business-specific query patterns
Understand domain-specific terminology
The Specialization Strategy
1. Schema Distillation
Instead of feeding the raw schema, create a rich schema representation:
2. Query Pattern Mining
Analyze existing queries to understand:
Most common JOIN patterns
Typical WHERE clause conditions
Frequently used aggregations
Business-specific requirements
Example Pattern:
3. Synthetic Data Generation
Create training data that matches your specific needs:
Template-Based Generation
Start with common query patterns
Vary the conditions and aggregations
Keep business rules intact
Natural Language Variation
Edge Case Coverage
Null handling
Date range edge cases
Complex filtering conditions
Fine-tuning Approach
1. Progressive Specialization
Start broad, then narrow down:
Phase 1: Schema Understanding
Train on simple schema navigation
Focus on table relationships
Master basic queries
Phase 2: Query Patterns
Introduce common business queries
Learn typical aggregations
Master JOINs specific to your schema
Phase 3: Edge Cases
Handle complex conditions
Learn business rules
Master error cases
2. Data Augmentation Techniques
Question Paraphrasing
SQL Variation
Training Optimizations
1. Focused Learning
Use smaller batch sizes (8-16)
Higher learning rates early, then decay
Gradient accumulation for stability
2. Business Rules Integration
Encode business rules into the training:
3. Error Recovery
Train the model to fix common mistakes:
Validation Strategy
Business-Specific Test Set
Real queries from your system
Common user questions
Edge cases specific to your domain
Execution Testing
Test against actual database
Verify result correctness
Check performance implications
User Acceptance Criteria
Match specific formatting preferences
Follow naming conventions
Adhere to optimization guidelines
Deployment Considerations
Version Control
Track schema changes
Monitor query patterns
Update training data
Performance Monitoring
Track accuracy by query type
Monitor execution times
Log user corrections
Continuous Improvement
Collect user feedback
Add new patterns
Refine error handling
Key Success Factors
Quality Over Quantity
Few high-quality examples beat many poor ones
Focus on real-world usage patterns
Prioritize business-critical queries
Iterative Refinement
Start simple, add complexity gradually
Test thoroughly at each step
Incorporate user feedback
Domain Knowledge Integration
Embed business rules
Include domain-specific terminology
Mirror existing query patterns
Remember: The goal isn't to create a general-purpose SQL generator, but rather a highly specialized tool that excels at your specific use case.
Build AI enbaled apps from a single prompt
Build full stack Apps from prompts
READ OTHER POSTS